Welcome to Tech Legal Experts, a platform where technology seamlessly integrates with expert legal knowledge to address the demands of today’s dynamic world. Our mission is to offer innovative insights and informational resources, empowering individuals and businesses to navigate legal complexities with assurance. By merging deep legal expertise with a forward-thinking approach to technology, Tech Legal Experts aims to be a trusted source for general Tech legal information and informed decision-making.
Tech Legal Experts is led by a seasoned legal professional with over 15 years of experience across diverse legal fields. A Ph.D. holder in Private Law from Grenoble University, our founder has built a distinguished career defined by precision, strategic thinking, and a dedication to excellence. Her profound understanding of both traditional legal frameworks and emerging challenges ensures the delivery of valuable informational resources to meet the needs of a rapidly evolving landscape.
Meet the Founder
Empowering Legal Clarity in the Digital Age
As the founder of TechLegalExperts, I am driven by a vision to make the law accessible, intuitive, and aligned with the needs of our digital age. This platform was created to empower individuals and businesses with the tools, information, legal templates and knowledge they need to navigate legal complexities confidently. TechLegalExperts combines advanced technology with trusted expertise, offering resources that break down barriers and simplify the legal journey. My goal is to ensure that everyone—whether protecting their rights, pursuing opportunities, or seeking clarity—has access to reliable legal resources. Together, we’re building a future where justice and progress go hand in hand.
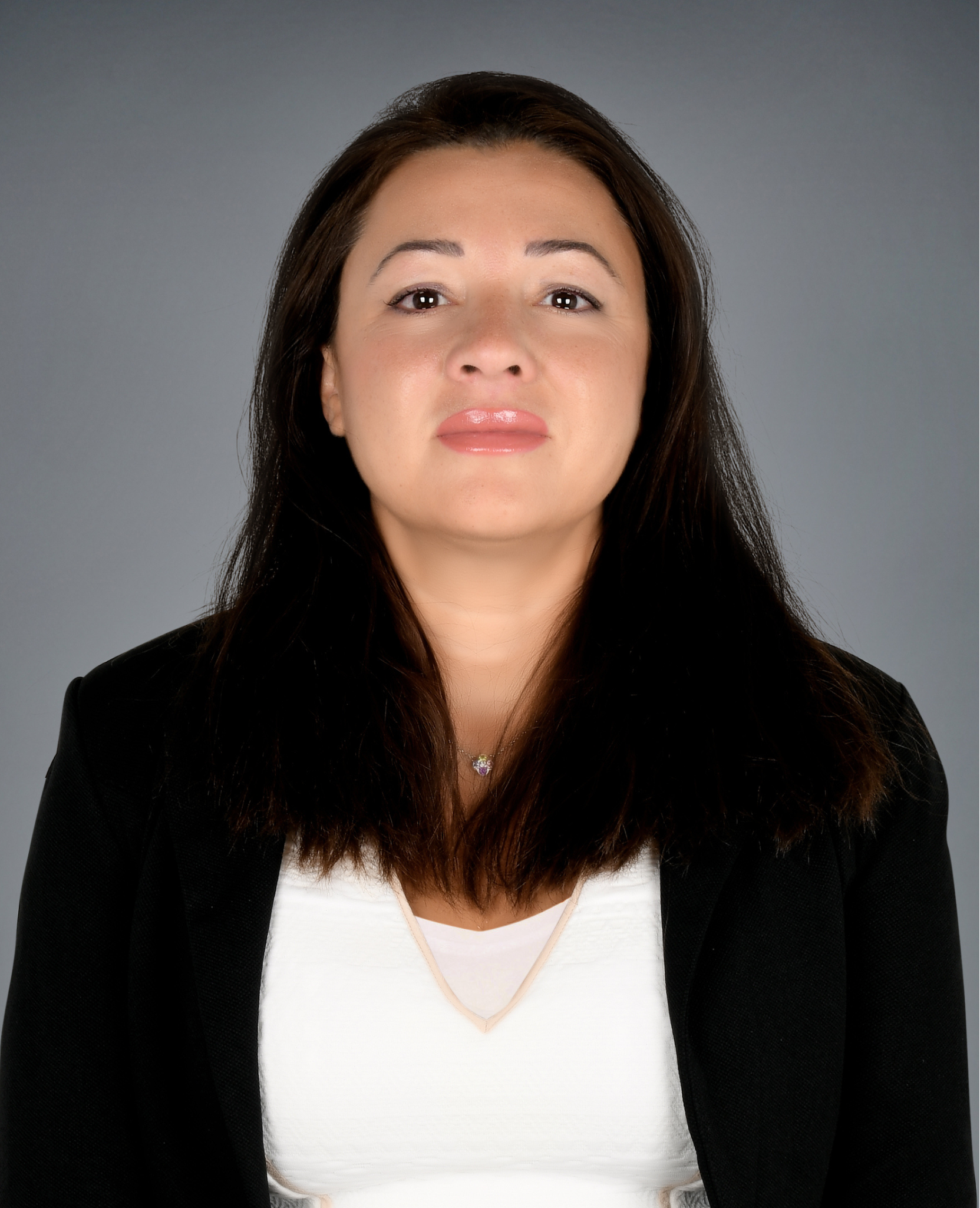
Marguerite Maroudis
Founder of TechLegalExperts

Contact Us
Check our FAQ
Get help from our AI chatbot or visit our FAQs for more answers.
Call us
Reach customer support at 971529575131, Monday through Friday, 8am to 6 pm (GMT+4)
Send an e-mail
Need more information? Send us a message via contact@techlegalexperts.com
FAQ
Top questions
What services does TechLegalExperts provide?
TechLegalExperts offers a range of professional tech legal information, including ready-to-use legal templates, compliance guidance, and contract drafting for blockchain and technology-related projects. Our services are designed to help businesses save time, reduce legal risks, and maintain compliance with local and international laws.
Are your legal templates compliant with local and international laws?
Yes, our legal templates are carefully crafted to align with local and international regulations, including UAE laws, GDPR, and other applicable frameworks. However, we recommend consulting a qualified legal professional to ensure they meet your specific needs and jurisdictional requirements.
In which languages are the legal templates available?
Our legal templates are available in English, Arabic, and French, making them accessible to a wide range of users across different regions and linguistic backgrounds.
Can I customize the templates to fit my specific needs?
Yes, our templates are designed to provide a solid legal foundation, but they are downloadable in PDF format, which means they cannot be directly edited. However, you can easily convert them into an editable format using PDF editing tools or retype the necessary sections to tailor them to your specific needs. If you require significant modifications, we recommend consulting a legal professional to ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
How can I access the templates or services on TechLegalExperts?
Accessing our resources is simple. Create an account on our platform, browse our library of legal templates, and download the ones that suit your needs.
Is TechLegalExperts suitable for businesses of all sizes?
Yes, TechLegalExperts is designed to serve individuals, startups, SMEs, and large corporations. Whether you’re just starting out or managing an established enterprise, our resources are scalable, and tailored to meet your needs.
For help with your TechLegalExperts account and related services, you may Contact Us for assistance Monday through Friday, 8 AM to 6 PM (GMT+4). Reach out via WhatsApp Business for chat-based support only at [00971 52 957 5131] or email us at contact@techlegalexperts.com.
Know more about us
Top questions in the Metaverse domain
What is the Metaverse, and why is it important?
The Metaverse is a virtual shared space where people interact through avatars, powered by augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). Its importance lies in its potential to transform social interactions, commerce, entertainment, and more.
What legal issues can arise in the Metaverse?
Key concerns include intellectual property rights, data privacy, cybersecurity, digital contracts, and disputes over virtual assets or real estate.
How are intellectual property rights protected in the Metaverse?
Intellectual property laws apply to virtual creations, but challenges arise due to jurisdictional differences and enforcement in a digital context.
What privacy risks exist in the Metaverse?
Users in the Metaverse may face heightened privacy risks, including unauthorized data collection, surveillance, and misuse of personal information.
Are transactions in the Metaverse legally binding?
Yes, digital contracts made in the Metaverse can be legally binding, provided they meet requirements like mutual agreement and consideration.
How is virtual property ownership regulated in the Metaverse?
Virtual property ownership is often governed by the terms and conditions of the platform, making it crucial for users to understand their rights before investing.
What role does cryptocurrency play in the Metaverse?
Cryptocurrency is commonly used for transactions in the Metaverse, raising legal questions about taxation, fraud prevention, and regulatory compliance.
Can laws vary across different Metaverse platforms?
Yes, each platform may impose its own rules and terms of service, which can lead to variations in user rights and responsibilities.
What steps can businesses take to protect their interests in the Metaverse?
Businesses should focus on securing intellectual property, ensuring compliance with data protection laws, and adopting robust terms of service for their virtual operations.
How can individuals and businesses prepare for the legal challenges of the Metaverse?
Staying informed, seeking professional legal advice, and carefully reviewing platform policies are essential to navigating the Metaverse confidently and securely.
Top questions in the AI domain
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, particularly computer systems. It includes tasks like learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and language understanding.
How is AI used in everyday life?
AI powers various applications, including virtual assistants, recommendation systems, chatbots, autonomous vehicles, fraud detection, and personalized marketing.
What are the ethical concerns surrounding AI?
Key concerns include bias in algorithms, lack of transparency, potential job displacement, and the ethical implications of AI decision-making.
How is AI regulated globally?
AI regulation varies by region, with some governments focusing on ethical guidelines, data privacy laws, and standards for AI deployment to ensure safety and fairness.
What is machine learning, and how is it related to AI?
Machine learning is a subset of AI that enables systems to learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed, using algorithms to analyze data and make predictions.
How does AI impact data privacy?
AI relies heavily on large datasets, raising concerns about data collection, storage, and usage, including potential breaches and misuse of sensitive information.
What industries benefit most from AI?
AI has significant applications in healthcare, finance, manufacturing, retail, education, transportation, and entertainment, among others.
What is the role of AI in cybersecurity?
AI enhances cybersecurity by identifying threats, detecting anomalies, automating responses, and predicting potential attacks based on patterns.
Can AI replace human jobs?
AI enhances cybersecurity by identifying threats, detecting anomalies, automating responses, and predicting potential attacks based on patterns.
What are the risks of AI development?
Risks include unintended consequences, lack of accountability, potential misuse of AI for malicious purposes, and challenges in ensuring AI systems are safe and unbiased.
Top questions in the Bitcoin domain
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that allows peer-to-peer transactions without the need for a central authority like a bank. It operates on blockchain technology.
How does Bitcoin work?
Bitcoin transactions are recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain. Miners verify transactions and add them to the blockchain using complex cryptographic algorithms.
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain is a decentralized, immutable digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers, ensuring transparency and security.
How can I buy Bitcoin?
Bitcoin can be purchased through cryptocurrency exchanges, peer-to-peer platforms, or Bitcoin ATMs using traditional currencies or other cryptocurrencies.
Is Bitcoin secure?
Bitcoin’s blockchain is highly secure due to its decentralized nature and cryptographic protocols. However, users must protect their wallets and private keys to avoid theft.
What determines the price of Bitcoin?
Bitcoin’s price is influenced by factors like supply and demand, market sentiment, macroeconomic trends, and regulatory developments.
Is Bitcoin legal?
The legality of Bitcoin varies by country. Some nations fully support its use, while others restrict or ban it. Always check local regulations before using Bitcoin.
What is Bitcoin mining?
Bitcoin mining is the process of verifying and adding transactions to the blockchain by solving complex mathematical problems. Miners are rewarded with new Bitcoins for their efforts.
What are the risks of investing in Bitcoin?
Risks include price volatility, regulatory changes, cybersecurity threats, and the potential for scams or fraudulent platforms.
How can I store Bitcoin safely?
Bitcoin can be stored in digital wallets, which come in various forms: hardware wallets, software wallets, and online wallets. Hardware wallets are considered the most secure.
Top questions in the Smart Contracts domain
What is a smart contract?
A smart contract is a self-executing contract with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. It automatically enforces and executes actions when predefined conditions are met.
How do smart contracts work?
Smart contracts run on blockchain networks. When specified conditions are met, the contract’s code executes the agreed-upon actions, such as transferring funds or verifying ownership.
What are the benefits of using smart contracts?
Benefits include automation, transparency, reduced reliance on intermediaries, cost savings, and increased efficiency in executing agreements.
Which blockchain platforms support smart contracts?
Popular platforms include Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Solana, Cardano, and Polkadot. Ethereum is widely known for pioneering smart contract technology.
What are some real-world applications of smart contracts?
Smart contracts are used in industries like finance (DeFi), supply chain management, real estate, healthcare, gaming, and digital identity verification.
Are smart contracts legally binding?
The enforceability of smart contracts depends on the jurisdiction. In many cases, they can complement traditional legal agreements if the terms are legally sound.
What are the risks of using smart contracts?
Risks include coding errors, vulnerabilities to hacking, reliance on oracles for external data, and challenges in updating or modifying deployed contracts.
What are oracles in the context of smart contracts?
Oracles are external services that provide smart contracts with real-world data, such as weather information, stock prices, or sports results, enabling them to interact with external systems.
Can smart contracts be altered or canceled?
Once deployed on the blockchain, most smart contracts cannot be altered due to the immutable nature of the blockchain. However, upgradable contracts or governance mechanisms can allow modifications.
How secure are smart contracts?
While the blockchain itself is secure, smart contracts are only as secure as their code. Proper auditing and testing are essential to minimize vulnerabilities and prevent exploitation.
What our customers are saying



DISCLAIMER: TechLegalExperts is not a legal or attorney website. All information provided on this platform is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice or consultancy services . Get more information about this disclaimer.
LEGAL NOTICE: TechLegalExperts is a brand operated under the registered name “TechLegalExperts Portal” in accordance with its commercial license.
